Access Menu
What is an angioplasty?
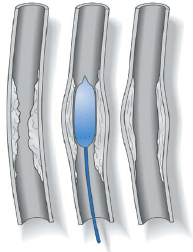 Angioplasty is a medical procedure that opens upblocked or narrowed blood vessels without surgery. An interventional radiologist, a doctor specially trained in minimally invasive, targeted treatments, performs this procedure. During the angioplasty, the interventional radiologist inserts a very small balloon attached to a thin tube (a catheter) into a blood vessel through a very small incision in the skin, about the size of a pencil tip. The catheter is threaded under X-ray guidance to the site of the blocked artery. When the balloon is in the area of the blockage, it is inflated to open the artery, improving blood flow through the area.
Angioplasty is a medical procedure that opens upblocked or narrowed blood vessels without surgery. An interventional radiologist, a doctor specially trained in minimally invasive, targeted treatments, performs this procedure. During the angioplasty, the interventional radiologist inserts a very small balloon attached to a thin tube (a catheter) into a blood vessel through a very small incision in the skin, about the size of a pencil tip. The catheter is threaded under X-ray guidance to the site of the blocked artery. When the balloon is in the area of the blockage, it is inflated to open the artery, improving blood flow through the area.
Why do I need angioplasty?
The most common reason for angioplasty is to relieve a blockage of an artery caused by atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). Atherosclerosis is a gradual process in which cholesterol and scar tissue build up inside the artery, forming a substance called “plaque” that clogs the artery. Arteries are like tubes; they carry blood and oxygen to the tissue in your body. When an artery becomes narrowed or blocked, the tissue supplied by that artery does not get enough oxygen.
The symptoms you feel depend on which artery is blocked. For example, a blocked artery in the legs may cause pain when you walk or even when you are resting in bed. A blocked artery to a kidney may cause high blood pressure. Some blockages are best treated with surgery, while others are best treated with angioplasty.
A member of the interventional radiology team – the doctor, nurse or technologist – will talk with you about the procedure in detail and answer any questions you have. The angioplasty procedure usually takes one to two hours to complete. In some cases, it may take longer.
What is an angioplasty like? Will it hurt?
If you have not had an angiogram (an X-ray examination of your arteries), the interventional radiologist will perform that procedure before proceeding with your angioplasty. An angioplasty has three major steps: placement of the angioplasty catheter into the blocked artery, inflation of the balloon to open the blocked artery, and removal of the catheter. Local anesthetic is used so that you will only feel some pressure during the procedure.
How do I prepare for the procedure?
If you are already a patient in the hospital, your nurses and doctors will give you instructions on how to prepare for your angioplasty. If you are being admitted to the hospital on the morning of your angioplasty, or if you are having your procedure done as an outpatient, follow these instructions, unless your doctor specifies otherwise:
Eating
Do not eat any solid food after midnight on the night before your procedure. You may drink clear fluids.
Medication
Most people can continue to take their prescribed medicines. If you are a diabetic and take insulin, ask your doctor about modifying your insulin dose for the day of your procedure. If you are taking the oral anti-diabetic medicine glucophage (Metformin), you will need to discontinue use for up to 48 hours prior to the procedure and 48 hours following the procedure. Consult with your doctor about blood sugar control during this period. If you take a blood thinner such as Coumadin, you must tell your doctor so that it can be stopped. Bring all your medications with you.
Allergies
If you are allergic to contrast (X-ray dye) or iodine, let your doctor know as soon as possible. If possible, let the interventional radiologist know about your allergy a few days before your angioplasty procedure. Your doctors can then plan to take special precautions during the procedure or prescribe special medications prior to the procedure.
Smoking
Do not smoke for at least 24 hours before your angioplasty. Blood tests are usually done the day before the angioplasty. Before your procedure, you will dress in a hospital gown and an intravenous (IV) line will be placed in one of your veins. You may need to remove your jewelry and any dentures or partials. The IV will be used to give you fluids and medicines during the procedure and will stay in place until after your angioplasty is completed.